How to operate a drone is a question many ask, bridging the gap between fascinating technology and practical application. This guide provides a structured approach to understanding drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic maneuvers to advanced techniques and safety regulations. Whether you’re a novice or seeking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to safely and effectively pilot your drone.
We will explore the nuances of different drone types, delve into essential flight controls, and highlight crucial safety protocols. Furthermore, we’ll uncover the intricacies of drone camera operation, enabling you to capture stunning aerial footage. This journey will not only equip you with the technical skills but also instill a deep understanding of responsible drone operation.
Drone Types and Their Operation
Understanding the different types of drones and their unique operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explore multirotor, fixed-wing, and hybrid drones, highlighting their differences in control, capabilities, and suitability for various applications.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of the fundamentals, and for a comprehensive guide, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on thorough preparation and practice.
Multirotor Drone Operation
Multirotor drones, commonly known as quadcopters (four rotors) or hexacopters (six rotors), are characterized by their vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) capability and exceptional maneuverability. Their multiple rotors provide redundancy, allowing for continued flight even if one rotor fails (depending on the number of rotors). Control is primarily achieved through manipulating the speed of individual rotors, enabling precise hovering, directional changes, and agile movements.
The control interface typically involves joysticks for directional control and buttons for additional functions like camera control and Return-to-Home (RTH).
Fixed-Wing Drone Operation
Fixed-wing drones, resembling miniature airplanes, require a runway or launch assist for takeoff and landing. Their flight is more akin to traditional aircraft, relying on aerodynamic lift generated by their wings. Control involves manipulating the ailerons, elevator, and rudder, similar to a manned aircraft. These drones are generally faster and have longer flight times than multirotors but lack their maneuverability and VTOL capability.
Their control interface might include a more complex setup, often incorporating trim adjustments and advanced flight parameters.
Hybrid Drone Operation
Hybrid drones combine features of both multirotor and fixed-wing designs. They typically utilize rotors for VTOL and transition to fixed-wing flight for longer range and endurance. Control involves a more complex interplay of rotor and aerodynamic controls, requiring a higher level of piloting skill. The transition between flight modes often necessitates precise timing and control adjustments.
Drone Type Comparison
| Drone Type | Pros | Cons | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multirotor | Easy to operate, VTOL, highly maneuverable, stable hovering | Shorter flight time, lower speed, susceptible to wind | Aerial photography, videography, inspection of small areas, search and rescue |
| Fixed-wing | Longer flight time, higher speed, greater range | Requires runway/launch assist, less maneuverable, not suitable for hovering | Aerial surveying, mapping, long-range surveillance |
| Hybrid | Combines VTOL and longer flight time, versatility | More complex to operate, higher cost, potential for system failure | Applications requiring both VTOL and long-range capabilities |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Thorough pre-flight checks are essential for ensuring safe and reliable drone operation. This section details crucial inspections, calibrations, and procedures to minimize risks and maximize flight success.
Pre-Flight Checklist

- Inspect propellers for damage or imbalance.
- Check motor functionality and mounting.
- Verify battery charge level and health.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Ensure GPS signal is strong and accurate.
- Review weather conditions and adjust flight plan accordingly.
- Check all communication links between the drone and controller.
- Confirm sufficient free space for operation.
Sensor and GPS Calibration
Accurate sensor and GPS data are vital for stable flight. Calibration procedures vary depending on the drone model, but generally involve a series of controlled movements and positioning to allow the drone’s internal systems to accurately determine its orientation and location. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
Battery Checks and Charging
Always use manufacturer-approved batteries and chargers. Before each flight, verify the battery level and health using the drone’s battery monitoring system. Proper charging procedures, as Artikeld in the manual, help extend battery life and prevent damage.
Propeller and Motor Inspection
Inspect propellers for any cracks, chips, or damage. Check motor mounts for tightness and ensure all motors spin freely without any binding or unusual noises. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
This section provides a step-by-step guide to mastering basic drone flight controls and maneuvers, laying the foundation for more advanced techniques.
Drone Controller Operation
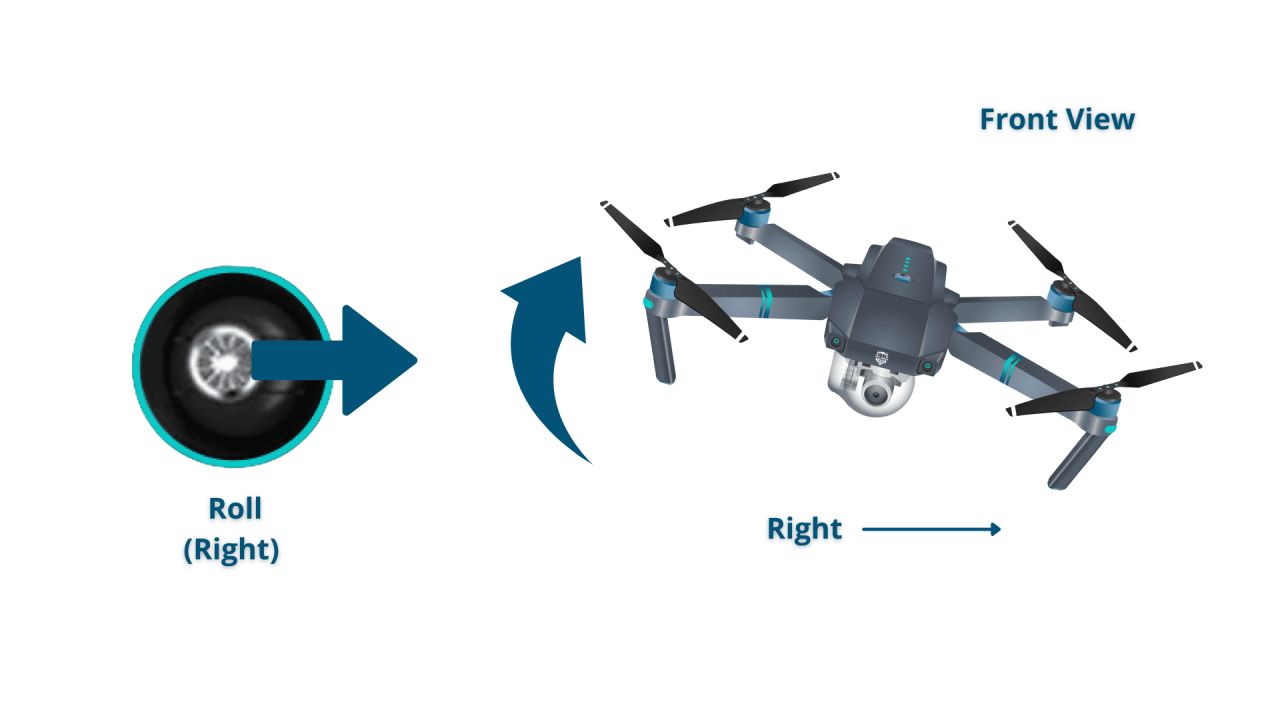
Most drone controllers use two joysticks. One typically controls the drone’s pitch and roll (forward/backward and left/right movement), while the other controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude). Buttons on the controller activate additional functions such as camera control, Return-to-Home (RTH), and emergency stops. Familiarize yourself with the specific controls of your drone model before attempting any flight.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
- Takeoff: Gently increase throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable altitude and position by precisely adjusting the throttle and directional controls.
- Directional Movement: Use the directional joystick to move the drone forward, backward, left, or right.
- Landing: Gradually decrease throttle to smoothly lower the drone to the ground.
Controlled Ascent and Descent
For controlled ascents and descents, smoothly increase or decrease the throttle, maintaining a steady rate of climb or descent. Avoid sudden throttle changes to prevent erratic movements.
Basic Maneuver Flight Plan
A safe and open area, free from obstacles and people, is essential for practicing basic maneuvers. Start with short, controlled flights, gradually increasing the duration and complexity as you gain confidence and proficiency. Begin by practicing hovering, then progress to directional movements and controlled ascents and descents. Always maintain visual contact with the drone and be prepared to land immediately if necessary.
Advanced Flight Techniques
This section explores more advanced flight maneuvers and techniques, expanding your drone piloting skills and capabilities.
Complex Maneuvers
Complex maneuvers, such as flips, rolls, and precision hovering, require significant practice and skill. These maneuvers are typically enabled through specific control inputs or modes within the drone’s flight controller. Always practice in a safe and open environment, away from obstacles and people. Start slowly and gradually increase the complexity of the maneuvers as your skill improves.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires careful control adjustments to maintain stability. Use precise inputs to counteract wind gusts and maintain the desired flight path. Be aware of wind speed and direction and adjust your flight plan accordingly. Consider postponing flight if wind conditions are excessively strong.
GPS Waypoints and Autonomous Flight
Many drones offer GPS waypoint functionality, allowing you to pre-program a flight path. This enables autonomous flights, freeing the pilot to focus on camera operation or other tasks. Plan your waypoints carefully, ensuring they avoid obstacles and remain within the drone’s operational range.
Return-to-Home (RTH) Functionality
The RTH function automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point. This is a crucial safety feature, particularly in case of signal loss or low battery. Ensure that the RTH function is properly configured and tested before relying on it in critical situations.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality photos and videos is a key aspect of drone operation. This section covers camera modes, settings adjustments, and techniques for optimal image capture.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone which will give you the confidence to fly safely and effectively.
Ultimately, responsible drone operation ensures both your safety and the safety of others.
Camera Modes and Settings
Most drone cameras offer various shooting modes (photo, video, timelapse, etc.) and settings (ISO, shutter speed, aperture, white balance). Understanding these settings is crucial for capturing high-quality images. Experiment with different settings to determine the optimal combination for various lighting conditions and subject matter.
Adjusting Camera Settings
ISO controls the camera’s sensitivity to light; higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but can introduce noise. Shutter speed determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light; faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. Aperture controls the amount of light entering the camera lens; wider apertures (smaller f-numbers) allow more light, resulting in shallower depth of field.
Capturing High-Quality Media
For high-quality photos, use a stable platform (consider using a tripod if possible) and avoid shooting in harsh sunlight. For videos, maintain smooth and steady movements. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create visually appealing footage. Consider using ND filters to control light exposure and achieve better video quality.
Transferring and Storing Media
Captured media can typically be transferred to a computer or mobile device via a microSD card reader or wireless connection. Always back up your media to multiple locations to prevent data loss.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount for responsible drone operation. This section Artikels essential guidelines and procedures for safe and legal drone flights.
Safety Regulations
Drone regulations vary by region. Familiarize yourself with the specific laws and regulations in your area before operating a drone. This typically includes registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and limitations on flight altitudes and distances. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation
- Obstacle Collisions: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles and always maintain visual contact with the drone.
- Loss of Control: Regularly check battery levels and signal strength. Be prepared to land immediately if necessary.
- Adverse Weather: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
- Privacy Concerns: Respect the privacy of others and avoid flying over private property without permission.
Safe Distance from People and Property
Maintain a safe distance from people and property during drone operation. Avoid flying over crowds or sensitive areas. Always be mindful of the potential impact of your drone on the environment and surrounding areas.
Emergency Procedures
In case of a malfunction or unexpected event, immediately initiate emergency procedures. This may include activating the RTH function, landing the drone in a safe location, or contacting emergency services if necessary. Practice emergency procedures regularly to ensure a swift and effective response in critical situations.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section Artikels maintenance schedules and steps for resolving common issues.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule includes cleaning the drone’s body and propellers, inspecting all components for damage, and lubricating moving parts as needed. The frequency of maintenance depends on the drone’s usage and environmental conditions. Consult your drone’s manual for specific recommendations.
Troubleshooting Common Issues, How to operate a drone
- Low Battery: Charge the battery using a manufacturer-approved charger.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure an unobstructed view of the sky and try recalibrating the GPS.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors for damage and replace faulty components.
- Communication Issues: Check the connection between the drone and controller, and ensure there is no interference.
Replacing Worn-Out Parts
Replace worn-out or damaged parts promptly. Use only manufacturer-approved replacement parts to ensure compatibility and safety.
Resources for Spare Parts and Maintenance
Spare parts and professional maintenance services are typically available from the drone manufacturer or authorized dealers. Online resources and forums can also provide valuable information and support.
Illustrative Examples of Drone Applications
This section provides detailed descriptions of various drone applications, showcasing their versatility and usefulness across diverse sectors.
Aerial Photography in a Cityscape
Imagine a drone, a sleek quadcopter with a high-resolution camera, hovering silently above a bustling cityscape at dusk. The camera, equipped with a wide-angle lens, captures a breathtaking panoramic view of skyscrapers illuminated against the twilight sky. The drone’s precise control allows the pilot to capture detailed shots of architectural marvels, bustling streets, and the city’s vibrant energy from unique, elevated perspectives.
Post-processing enhances the images, bringing out the city’s vibrant colors and textures, creating stunning aerial photography that captures the essence of urban life.
Bridge Inspection

A sturdy hexacopter drone, equipped with a high-definition camera and thermal imaging capabilities, is deployed to inspect a large suspension bridge. The drone, piloted remotely by an engineer, systematically flies along the bridge’s length and under its deck. The high-resolution camera captures detailed images of the bridge’s structural components, while the thermal imaging reveals any areas of potential heat loss or damage.
The collected data is then analyzed to assess the bridge’s structural integrity, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing potential safety hazards.
Package Delivery
A small, lightweight quadcopter drone, designed for short-range delivery, takes off from a designated launchpad. A small package, securely fastened to the drone’s undercarriage, is being delivered to a nearby residential address. The drone utilizes GPS navigation to autonomously navigate through the air, avoiding obstacles and adhering to pre-programmed flight paths. Upon reaching its destination, the drone gently lowers the package, completing a successful and efficient delivery, showcasing the potential of drone technology in streamlining logistics and delivery services.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding experience, opening up a world of possibilities for photography, videography, inspection, and more. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, focusing on safety, and continually practicing, you can confidently and responsibly navigate the skies. Remember that responsible operation includes adhering to local regulations and always prioritizing safety above all else. Enjoy the flight!
FAQs
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners. Look for features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home, and intuitive controls. Research reviews and compare models based on your budget and needs.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions (wind, payload). Expect flight times ranging from 15-30 minutes, but always check the manufacturer’s specifications.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point if GPS signal is lost. However, it’s crucial to remain vigilant and practice safe flying habits.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures.
