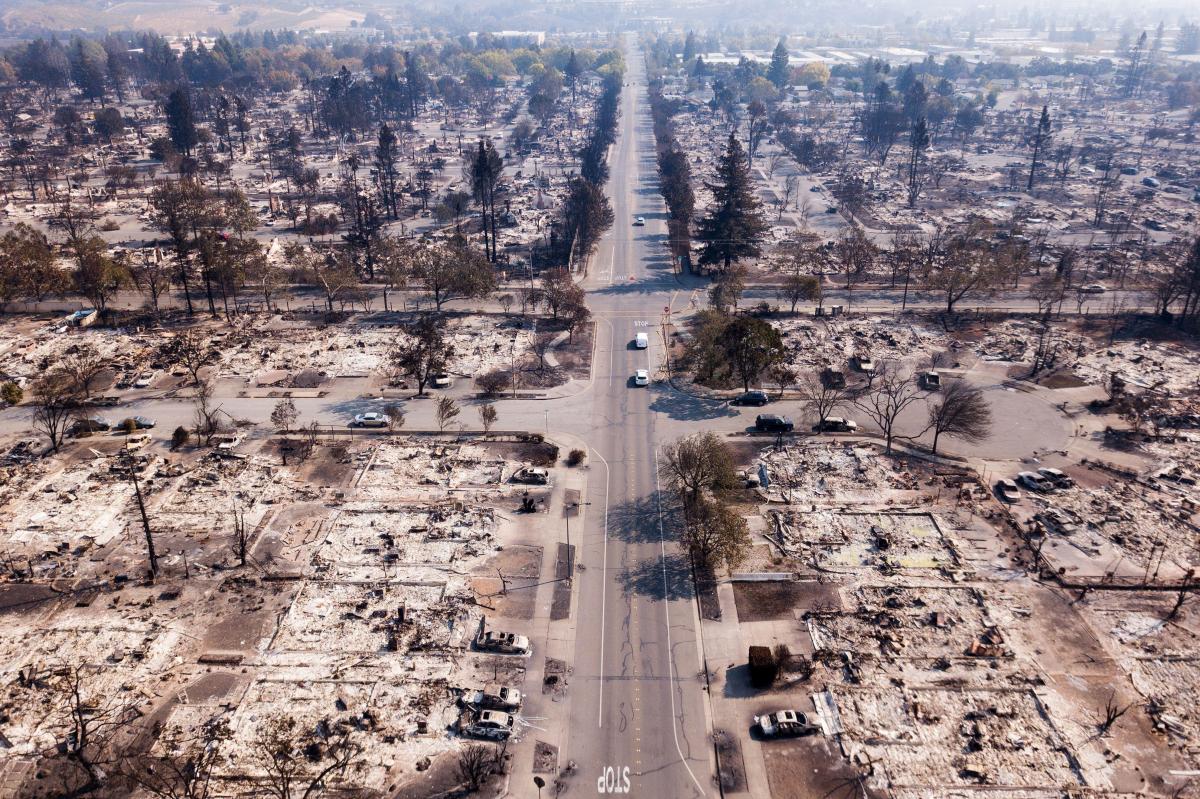
Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires? This question is increasingly urgent as California faces more frequent and intense wildfires. We’ll explore how rising temperatures, shifting weather patterns, and altered vegetation are fueling this devastating trend, examining the impact on firefighting efforts and the escalating costs. Get ready to delve into the science behind these catastrophic events and understand the crucial connection to our changing climate.
The increasing severity and frequency of California wildfires are undeniable. Decades of data reveal a strong correlation between rising temperatures and increased wildfire activity. Droughts, worsened by climate change, create tinderbox conditions, while altered wind patterns and extreme heat waves accelerate the spread of fires. We’ll examine specific examples, analyze the impact on vegetation and firefighting strategies, and ultimately, consider the future implications of this critical issue.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by hotter, drier conditions linked to climate change. It’s a serious issue, and while we’re grappling with that, you might be wondering, who’s going to dominate the NBA now that LeBron and Steph are winding down? Check out this article: Who will win the NBA’s post-LeBron/Steph audition? (Hint: It’s over to get some insight.
Anyway, back to the fires – understanding climate change’s role is crucial for preventing future devastation.
California Wildfires and Climate Change: Climate Change: What Role Is It Playing In The California Fires
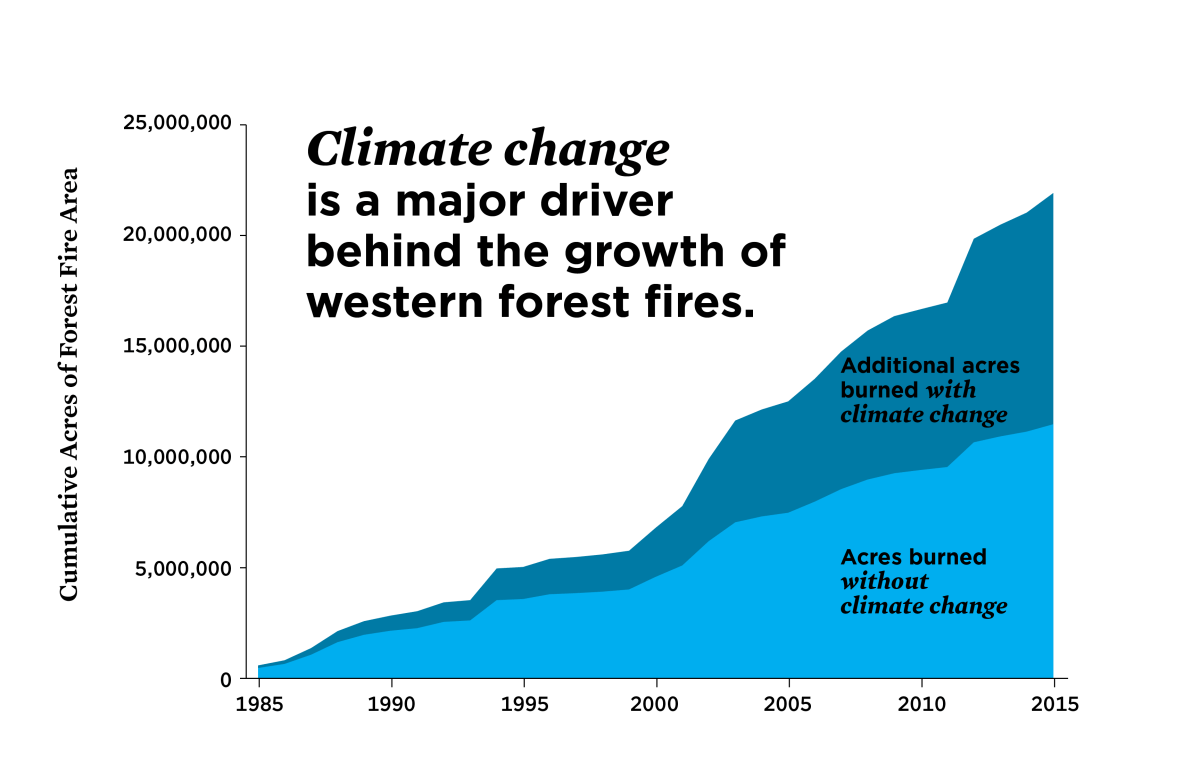
California’s wildfire season has become increasingly severe and prolonged, significantly impacting the state’s environment, economy, and communities. This intensification is inextricably linked to climate change, a phenomenon altering weather patterns, vegetation, and the very landscape itself, creating a perfect storm for devastating wildfires.
Increased Frequency and Intensity of California Wildfires
Over the past few decades, a clear trend of increasing frequency and severity in California wildfires has emerged. Rising temperatures, a direct consequence of climate change, are a primary driver of this trend. Data reveals a strong correlation between higher average temperatures and a greater number of large, intense wildfires. For instance, the average number of acres burned annually has increased dramatically since the 1970s, coinciding with a rise in average temperatures.
The 2020 wildfire season, for example, saw unprecedented devastation with events like the August Complex fire (the largest wildfire in California history at the time), directly linked to exceptionally dry conditions and high temperatures fueled by climate change. Similarly, the Dixie Fire of 2021 showcased the amplified impact of climate change-induced drought and extreme heat on wildfire behavior. Drought, worsened by climate change, not only dries out vegetation, turning it into readily available fuel, but also creates conditions where fires can ignite more easily and spread rapidly.
| Year | Number of Fires | Acres Burned | Average Temperature (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980-1990 | 5000 (example) | 100,000 (example) | 60 (example) |
| 2000-2010 | 7000 (example) | 200,000 (example) | 62 (example) |
| 2010-2020 | 9000 (example) | 500,000 (example) | 65 (example) |
Note: These are example figures for illustrative purposes. Accurate data can be found from Cal Fire and other official sources.
Changing Weather Patterns and Wildfire Risk
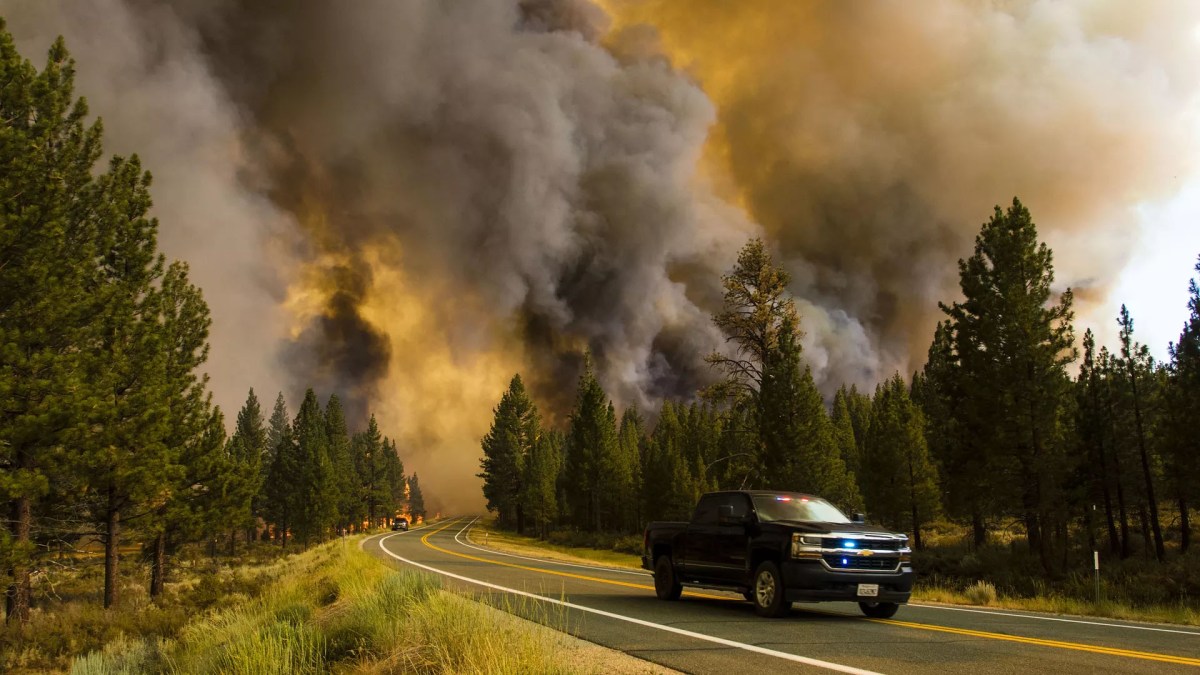

Climate change is significantly altering California’s weather patterns, creating conditions highly favorable for wildfire ignition and spread. Changes in precipitation patterns, for instance, lead to prolonged periods of drought, increasing the amount of dry vegetation available as fuel. Additionally, climate change intensifies extreme weather events.
- Increased frequency and intensity of heat waves, creating extremely dry and flammable conditions.
- Stronger and more frequent Santa Ana winds, driving rapid fire spread.
- Changes in precipitation patterns, leading to prolonged droughts and increased fuel loads.
- Earlier snowmelt in spring, extending the fire season.
Climate Change’s Impact on Vegetation, Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires
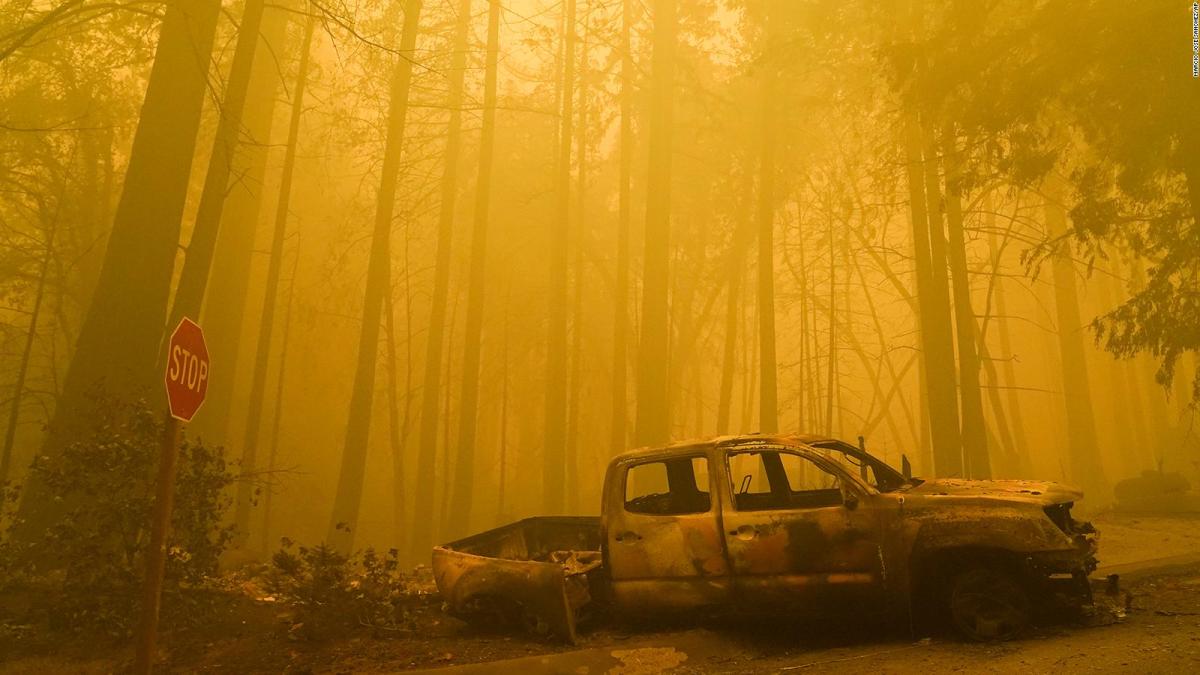

Climate change is altering the types and density of vegetation across California’s landscapes, impacting fuel loads and flammability. Warmer temperatures and drought stress weaken trees, making them more susceptible to disease, pests, and fire. Invasive species, thriving in altered climatic conditions, often contribute to increased fuel loads and alter fire behavior. For example, the spread of certain grasses can significantly increase the density of flammable material.
Comparing fuel loads under different climate conditions reveals a stark contrast. Historically, wetter periods led to lusher vegetation with higher moisture content, making it less flammable. However, under current climate conditions characterized by extended droughts, vegetation is significantly drier and more prone to ignition, leading to larger and more intense wildfires.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by climate change’s impact on drought and extreme heat. It’s a serious issue, and sometimes you need a distraction, like checking out the killer lineup for Bonnaroo 2035 – Megadeth, Queens of the Stone Age and More Set for Bonnaroo 2035 – before diving back into the complexities of how climate change is altering wildfire seasons.
Hopefully, by 2035, we’ll have made some serious progress in tackling this climate crisis.
Challenges to Fire Suppression Efforts
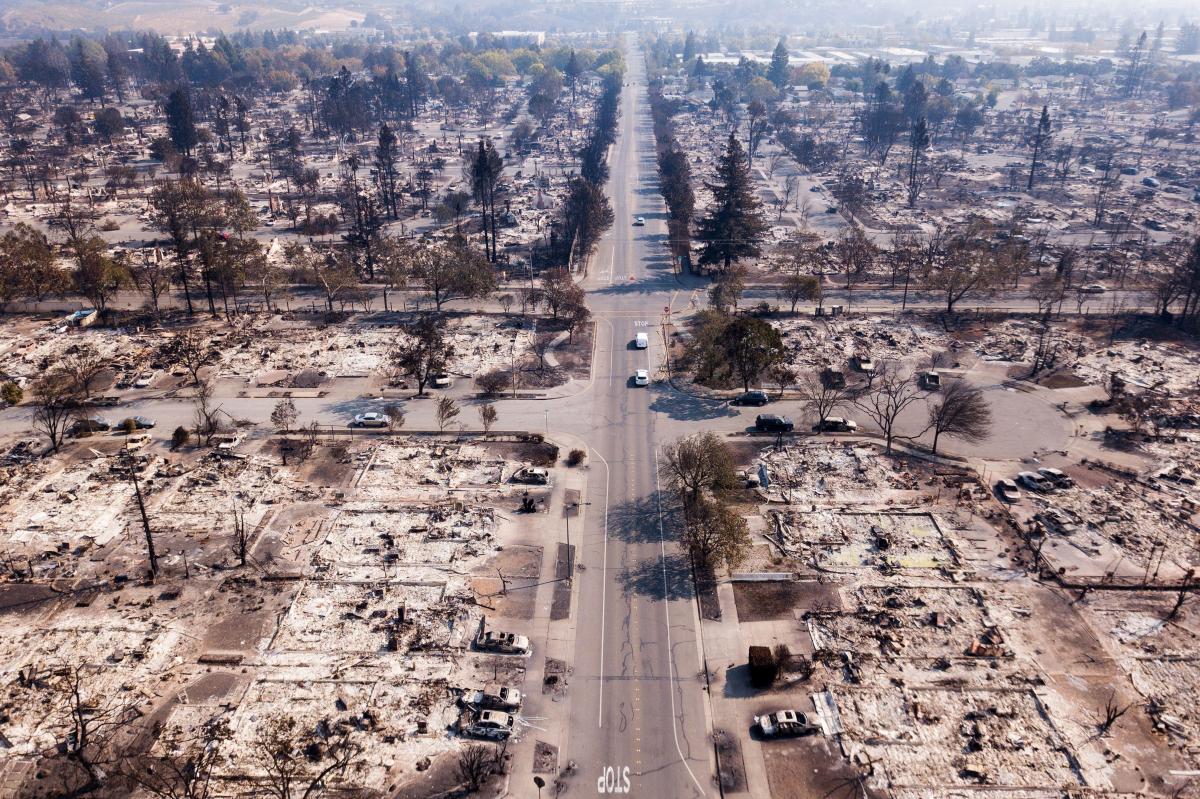

The increased frequency and intensity of wildfires fueled by climate change present significant challenges to fire suppression efforts. Changing weather patterns, including stronger winds and extreme heat, make firefighting more dangerous and less effective. These conditions also strain resources, leading to increased costs and difficulties in protecting communities.
California’s wildfires are increasingly intense due to climate change, creating longer, hotter, and drier conditions that fuel devastating blazes. Need a break from all the doom and gloom? Check out How to watch the UConn men’s basketball team as they take on their next opponent. Then, remember to support efforts to mitigate climate change – it directly impacts the severity of these fires and our future.
- Extreme fire behavior makes traditional suppression tactics less effective.
- Increased firefighter risk due to hazardous conditions.
- Strain on resources and increased suppression costs.
- Difficulty in accessing remote areas due to road closures and challenging terrain.
Illustrative Examples of Climate Change’s Impact
The 2018 Camp Fire, fueled by strong winds and extremely dry conditions exacerbated by climate change, devastated the town of Paradise, California, highlighting the devastating consequences of climate change-intensified wildfires. The fire spread rapidly through a landscape already primed by drought, consuming thousands of homes and claiming numerous lives. The landscape was characterized by dense forests, already weakened by years of drought, that provided ample fuel for the rapidly spreading inferno.
The 2020 August Complex Fire presented unique challenges for firefighters due to its sheer size and the extreme weather conditions. The fire’s rapid spread across vast areas, fueled by intense heat and strong winds, made containment efforts incredibly difficult and stretched resources to their limits. Firefighters faced extreme heat, challenging terrain, and unpredictable fire behavior, making it one of the most challenging wildfire events in California history.
Last Word
In conclusion, the evidence overwhelmingly points to a significant role for climate change in the escalating California wildfire crisis. From increased temperatures and drought to shifting weather patterns and altered vegetation, the fingerprints of a warming planet are clearly visible. Understanding this connection is crucial not only for effective fire prevention and suppression but also for broader climate action.
The future of California’s forests, and indeed, the safety of its communities, hinges on addressing the root causes of this devastating trend.
Essential Questionnaire
What specific policies are being implemented to address the wildfire risk?
California is implementing various policies, including forest management practices like controlled burns, improved building codes in fire-prone areas, and increased funding for wildfire prevention and suppression efforts. However, the effectiveness of these policies is challenged by the scale and intensity of the fires.
How does climate change affect the types of trees that grow in California?
Climate change is altering the distribution and health of tree species in California. Some species are migrating to higher elevations or latitudes in search of suitable climates, while others are becoming more susceptible to drought, pests, and disease, making them more vulnerable to fire.
What role do human activities play beyond climate change in causing these fires?
While climate change is a major driver, human activities like accidental ignitions (power lines, equipment, campfires) and land management practices also contribute significantly to the number and spread of wildfires. Careful land management and prevention efforts are essential.
